Even though today the information about different countries, places, nations, and ethnicities is very easy to find, there is frequent confusion about who were the Slavs and who are the Slavic peoples and which are the Slavic nations.
Slavic peoples are the people who speak some of the Slavic languages and mainly live on the territory of the Slavic nations.
If you have absolutely no idea what is a Slav, there are numerous positive, funny, or offensive stereotypes. For example, you can assume that a person who speaks Russian or a language that reminds of Russian is a Slav.
And if the subject interests you further, well then, here’s some information about the Slavic history, origins, language, territory, and religion.
Table of Contents
History and Origins of the Slavic Peoples
Slavs are the people who speak the languages that belong to the Balto-Slavic group of languages that belong to the Indo-European language family.
There isn’t much information about the Slavs before the Byzantine written records from the 6th century. It is widely assumed that the Slavs started descending from the Carpathian mountains in the 5th century and migrated in different directions. Until the 10th century, they have settled mainly on the territories abandoned by the German tribes that were fleeing from the Huns and their allies.
The Slavic tribes inhabited the territories between the Black Sea, the Ionian Sea, the Balkan Mountains, and the Baltic. Today, they are divided into three large subgroups, according to their geographical position and the similarities of their languages:
- East Slavs (Russians, Ukrainians, and Belarussians)
- West Slavs (Czechs, Poles, Slovaks, and Sorbs)
- South Slavs (Bosnians, Croatians, Slovenes, Serbians, Montenegrins, Macedonians, and Bulgarians)
It has to be noted that this classification is based mainly on the similarities of the language. There are many ethnic and linguistic sub-divisions within these groups, that are very complex.
Slavic Languages
The Slavic Languages are a group of languages from the Indo-European family. They are divided into three main groups:
| East Slavic | West Slavic | South Slavic |
|---|---|---|
| Belarussian | Czech-Slovak – Czech – Slovak | Eastern – Bulgarian – Macedonian – Church Slavonic |
| Russian | Lechitic – Polish, Silesian – Pomeranian – Kashubian | Western – Serbo-Croatian – Serbian – Croatian – Bosnian – Montenegrin – Burgenland Croatian – Slovene |
| Ukrainian | Sorbian – Upper Sorbian – Lower Sorbian | |
| Rusyn (there is a debate whether this is a separate language or a dialect spoken by the Rusyns people) |
Early or Ancient Slavs
It is really hard to determine who the Slavs were before the 6th century as there aren’t many sources in which one can root their studies. Historians, archaeologists, ethnographers, linguists, anthropologists, sociologists, and writers have been puzzled for centuries by the proto-Slavic language, Slavic origin, migrations, customs, social structure, and religion.
The earliest written data about the Slavic people describe them as “primitive and wild” invaders. In the Byzantine writings, they were described as “barbarian”. They were wildly attacking Roman settlements in order to conquer some lands, so the description might be accurate in the sense of the Slavic combativeness, but doesn’t say much about who they were, except that they annoyed the Romans.
Since there is scarce information about their origin, social life, and migration, authors quite often disagree. Some say that the ancestors of the Slavs had permanent settlements located around swamps and in the forests, while others argue that the Slavs were nomads.
Also, there are historians who believe that they were ruled by one ruler, presumably a king, with a treasury and defense force; while others claim that as soon as they settled in the territories of central Europe, they accepted some form of democracy and class differentiation.
Where Did Slavs Come From
The precise proto-Slavic location has been argued by historians, ethnographers, and archaeologists (as everything else for that matter). There have been theories that the Slavs originate from territories in the Near East, or in Russia. However, these theories have been discarded.
The majority of scholars who study the subject agree that the Slavs homeland is somewhere between Central and Eastern Europe, most likely within the heights of the Carpathians Mountains. This is the only territory from where the Slavs could reach Bohemia (and beyond) in the west, Volga River in the east, the Baltic Sea in the north, the Balkan Mountains in the south, and the Dinaric Alps in the southwest.
Slavic People and Countries Today
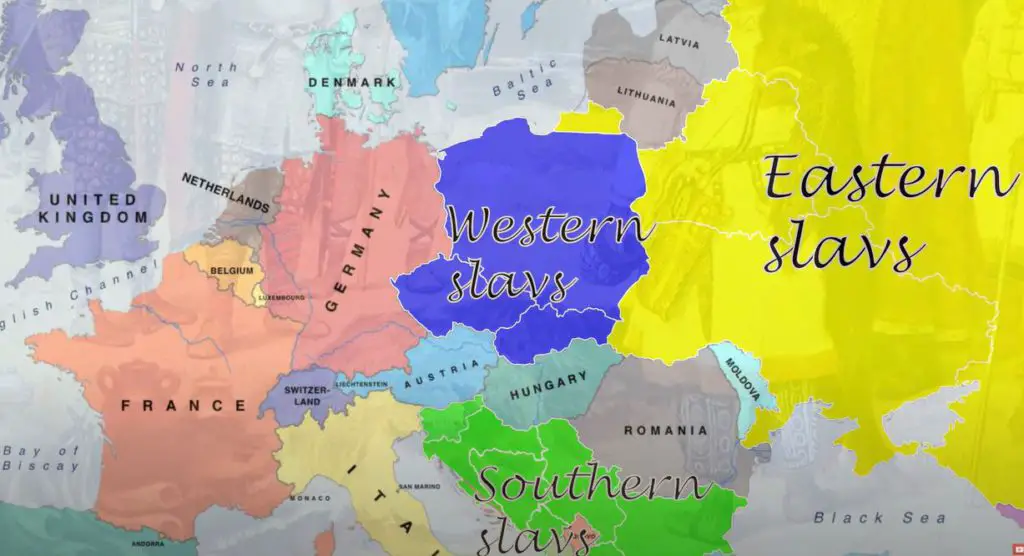
Today, the Slavic peoples live on the territory of Poland, Czech Republic, Slovakia – and are considered West Slavs; Ukraine, Belarus, Russia – East Slavs; Slovenia, Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Serbia, Montenegro, North Macedonia, and Bulgaria – the South Slavs. All of these are known as Slavic countries, and some refer to the region as the Slavic region.
Naturally, these three groups share numerous similarities but also differences as they have mixed with different tribes and ethnicities throughout the centuries. Hence, their classification as Slavs is based on the Slavic languages and presumed proto-cultural and genetic characteristics.
The Western Slavs have mixed with Prussians, Celts, Pannonian Avars, Hungarians, and Germanics. They were under the influence of the Western Roman Empire and the Catholic Church.
The Eastern Slavs in Eastern Europe have mixed mainly with Finno-Ugric peoples and Baltic people. Further East, on the territory of Russia, they have also mixed with Scythians, Siberians, Caucasian peoples, and Turkic peoples. They were influenced by the Byzantine Empire (The East Roman Empire) and the Eastern Orthodox Church.
And the South Slavs have mixed with Celtic tribes, East Germanic tribes, Asiatic (mostly Caucasian) tribes, as well as Proto-Balkan tribes (Hellenic, Paeonian, Thracian, Dacian, and Illyrian). During the time of the Ottoman occupation in the Balkan, they also mixed with Turks. They were influenced by the Byzantine Empire and the Eastern Orthodox Church, as well as the Ottoman Empire and Islam.
With exception of the Slovenes and Croats (who were influenced by the Western Roman Empire, and the Catholic Church.
Read: Slavic Names Explained With Examples
East Slavs
They occupy the territory of Belarus, Ukraine, and most of Russia and speak one of the East Slavic languages.
Over 81 percent of the people in Russia are considered Russians, meaning that they speak the Russian language, therefore most of them are considered Slavs. However, the remaining 19 percent are Tatars, Ukrainians, Bashkirs, Chuvashes, and other ethnicities.
The Russian language is also spoken in some of the countries of the former USSR such as Uzbekistan, Kazakhstan, Turkmenistan, Tajikistan, Georgia, Armenia, Azerbaijan, Moldova, Latvia, Lithuania, and Estonia. In these countries, there are populations that still speak the Russian language, but ethnically, they don’t consider themselves Russians or Slavs.
Slavs in Central Europe
The Slavs living in the Central part of Europe are considered west Slavs and speak Czech, Polish or Slovakian. They use the Latin alphabet and are mostly Catholic.
These nations have maintained strong relations with Europe, they often consider themselves as Europeans with a distinct ethnicity from what is categorized as Slavonic.
Of course, they still have physical features that are typical for the Slavs, but their economical and social development have caused more frequent interaction with Western European nations.
Younger generations have the tendency to speak of their ancestry as Slavic, but they do not feel much connection with the Slavic cultures. Anyways, in the language tree, they still belong to the Slavic group.
There are many interesting last names from this part of Europe. If you want to find out what are the most common Eastern European last names, read this article.
Southern Slavs
The South Slavic nations, with the exception of Bulgaria, were united in Yugoslavia, a country in Southeast Europe and Central Europe for most of the 20th century. Part of this union were Croatia, Slovenia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Serbia, North Macedonia, and Montenegro.
The country fell apart in the 1990s due to internal affairs.
There are numerous subgroups within the frame of this group and divisions that are based on genetics, religion, language, and ethnicity. This is the most complex subgroup of the Slavic group as it has been influenced by several very diverse cultures – Byzantine, Ottoman, Greek, and Proto-Balkan.
For example, there are the Bosniaks, South Slavs that ethnically identify with Bosnia and Herzegovina, but religiously identify themselves as Muslims and maintain relationships with Islam countries – through relatives, education, business, financial support, and migrations.
Then, there are people who identify themselves as Turks, only because their ancestors have accepted Islam during the Ottoman expansion in the Balkan region. They speak some of the Slavic languages, don’t speak Turkish, have never been to Turkey, do not have genetic relations with the Turks, and yet identify themselves as Turks.
And there are many ethnical groups that similarly identify themselves with a certain nation, religion, or culture, which is often an exception from the beliefs of the majority.
The Mythology of the Slavic Peoples
The Slavs were pagans with numerous deities. To this day, there are traces of pagan rituals and customs (still celebrated) across the territories where Slavs live. Many places (mainly small towns and villages) are famous for some of the yearly pagan rituals of the Slavic people that celebrate the changes of seasons. These events are followed with a lot of music, dance, masks, food, and alcohol, and are visited by a great number of people from domestic countries and abroad.
Perun
He is the supreme god of thunder and lightning who owned the sky. He is the equivalent of the Greek Zeus and the Roman Jupiter. He is represented as a warrior with muscles and a copper beard. He is represented either with a sledgehammer or a bow and arrow.
Dazhbog
Literally translated, this is “The Giver God” who gave people the sun and wealth. According to the Slavic folklore, this god is reborn every day and grows older as the day goes. He is dying at sunset only to be born again with the sunrise. He is often depicted with a sun halo around his head and a sun orb in his hand.
Stribog
This is the son of Perun and the god of wind, air, and sky. He is described as distasteful of other gods and doesn’t enjoy their company, however, he is quick to show up upon being called. He is usually depicted as an old man, holding a hunting horn with which he calls the wind.
These deities go further and are quite similar to gods and goddesses in different mythologies. The interesting part in the Slavic traditions are the rituals and customs dedicated to these deities, that have been celebrated throughout the year (when needed).
Today, most Slavs are traditionally Christian.
Conclusion
So, Slavs are people, descendants of a pro-Slavic tribe that lived in the Carpathian mountains until around the 5th century. Then, they started a movement towards regions of Bohemia, the Balkans, and Russia.
In the new settlements, they mixed with the inhabitants, members of different ethnicities, and accepted some of their social and cultural characteristics.
Unless otherwise noted, it is hard to define mutual characteristics for all Slavs, except that they share languages that are somewhat similar and are called Slavic languages.
Today, there is a complex ethnical diversity, but most of the Slavs identify with one of the Slavic nations.













